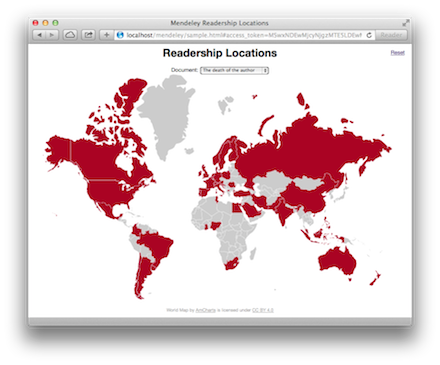
3. Request catalog document statistics and use the results to mark regions on a map
Whenever the user selects a new document, or immediately after the document popup menu is populated,
the reading statistics for the newly selected document are loaded with the help of the Javascript
SDK. The
reading statistics are used to color regions of the map. The JavaScript function
getCatalog sends the API request and calls updateMap to color maps regions
on
a successful response:
var getCatalog = function (event) {
var identifierType = this.selectedOptions.item(0).dataset.identifierType,
identifierValue = this.value,
uriArgs = {};
uriArgs[identifierType] = identifierValue;
uriArgs["view"] = "stats";
MendeleySDK.API.catalog
.search(uriArgs)
.done(updateMap)
.fail(errorHandler);
event.preventDefault();
}
First the function obtains the identifier type and value stored in the popup menu. Next the function
creates an array with this information and passes it as argument to the search method.
To be more precise, the URL will contain the following settings:
- the identifier type and value to search for a single document with a matching identifier
- the value of the
view field in the query string to stats to include
reading statistics in the response
The updateMap function looks like this:
var updateMap = function (stats) {
var arrayData = {},
maxCount = 0,
ratio;
$.each(stats, function(i, obj) {
if (obj.reader_count_by_country) {
for (var property in obj.reader_count_by_country) {
if(arrayData[property]) {
arrayData[property] += obj.reader_count_by_country[property];
} else {
arrayData[property] = obj.reader_count_by_country[property];
}
maxCount = Math.max(maxCount, arrayData[property]);
}
}
});
var map_regions = map.contentDocument.getElementsByClassName('land');
for (var index = 0; index < map_regions.length; index++) {
var map_region = map_regions[index].getAttribute("title");
if (arrayData[map_region]) {
ratio = arrayData[map_region]/maxCount;
map_regions[index].style.fill = "rgba(157, 22, 32, " + ratio + ")";
} else {
map_regions[index].style.fill = "rgb(204,204,204)";
}
}
}
If the API response is successful, an array containing the total number of readers by country is
built
using the data. This is an array with keys labelled with English descriptions of the
country
and the corresponding value is an integer indicating the number of times a document has been read.
After that, the function simply looks for matches between the region title label in the
SVG
map and the country member label in the /catalog API response:
** API response **
"reader_count_by_country": {
"Ireland": 2,
"United Kingdom": 1
}
** SVG document **
<path id="GB" title="United Kingdom" class="land" d="M459.38,281l-1.5,3.29l-2.12,-0.98l-1.73…" />
<path id="IE" title="Ireland" class="land" d="M457.88,284.29L458.34,287.65L456.22,291.77L451…" />
The function also calculates a ratio of readers distribution and uses an alpha value when coloring
the
map so that it reflects the relative number of readers
As geographic regions without reading statistics are not included, the function simply iterates
through
the map regions and if a reading statistic country is found, the function sets the map region's SVG
fill
color to red. If no country entry is found, the SVG map region is filled gray.